Project MNiSW 1584/B/P01/2008/35
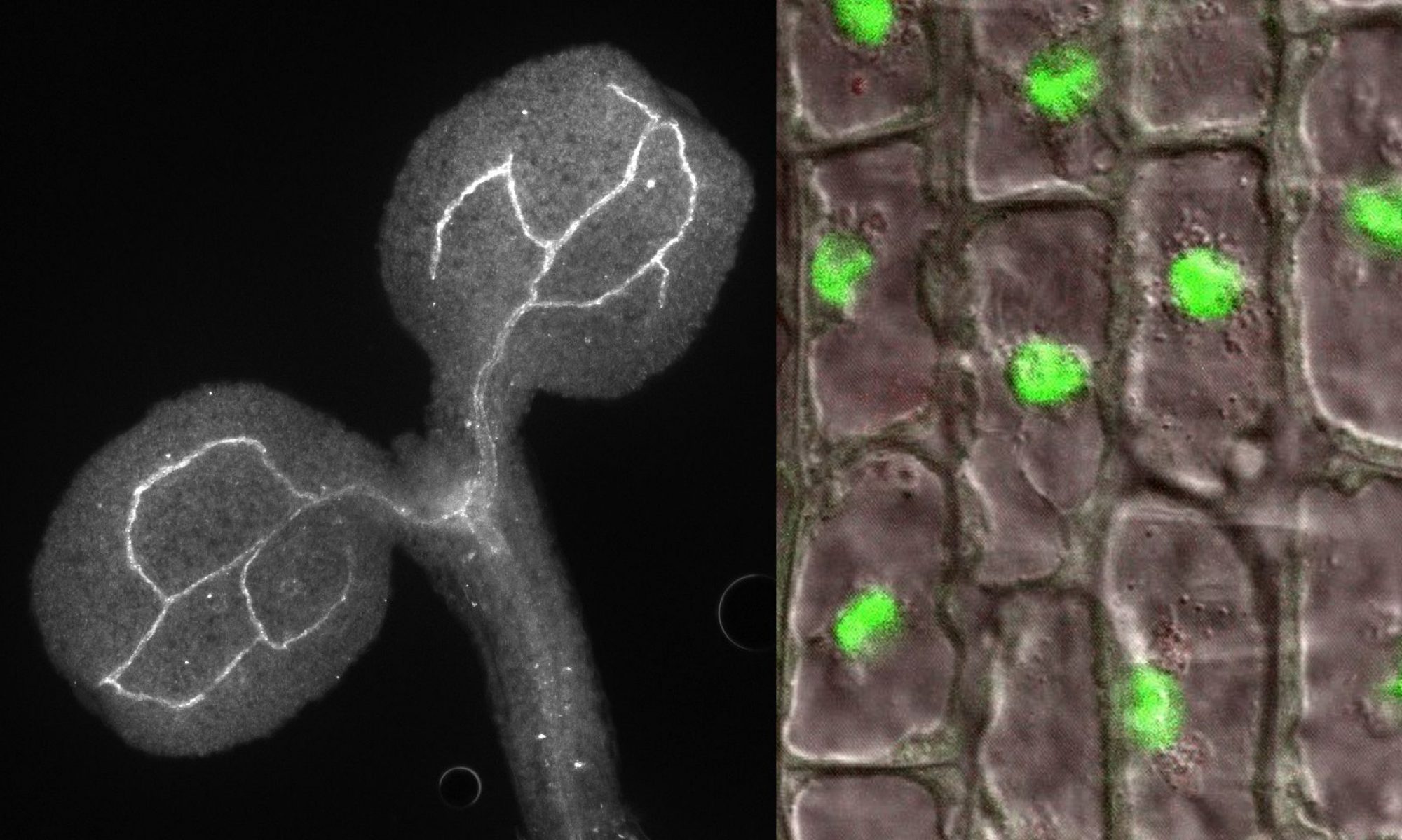
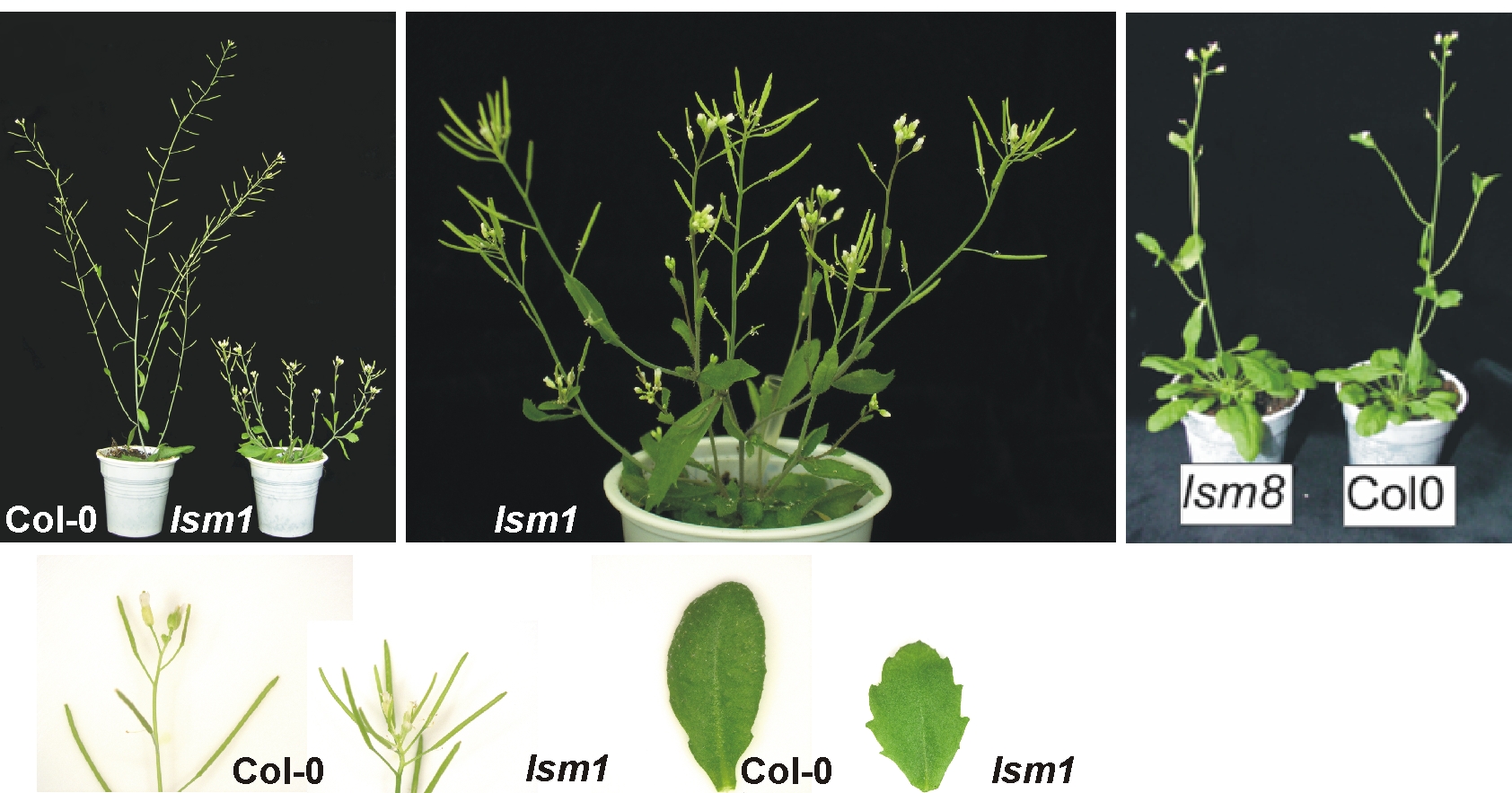
Although LSM (Sm-like) proteins are evolutionary conserved and described in detail in many eukaryotic organisms, they have not yet been characterized in plants. Our systematic research has led to a significant increase in knowledge about the function of LSM complexes in Arabidopsis. We have shown that AtLSM8 proteins, which are located only in the nucleus, and AtLSM5 found in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus, are involved in pre-mRNA assembly, while AtLSM5 and specifically cytoplasmic AtLSM1 contribute to 5′-3′ mRNA decay. In lsm8 and sad1 / lsm5 mutants, U6 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) was reduced and unspliced mRNA precursors accumulated, whereas mRNA stability was mainly affected in plants lacking AtLSM1 and AtLSM5. Some of the mRNAs affected in lsm1a lsm1b and sad1/lsm5 plants were also substrates of the cytoplasmic 5’–3’ exonuclease AtXRN4 and of the decapping enzyme AtDCP2. Interesting is the new observation that some substrates are also stabilized in plants lacking the AtLSM8 protein, suggesting that it is involved in the degradation of mRNA in the nucleus. The location of LSM components, purification of LSM-interacting proteins and analysis of their function by examining lsm mutants strongly suggest that also at least two complexes exist in plants: AtLSM1-7 and AtLSM2-8, involved in various aspects of RNA metabolism.
Golisz A, Sikorski PJ, Kruszka K, Kufel J (2013) Arabidopsis thaliana LSM proteins
function in mRNA splicing and degradation. Nucleic Acids Res 41, 6232-49.
Moreover, components of the 5′-3′ mRNA decay pathway, DCP5, LSM1-7 and XRN4, contribute to a proper response to a key plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA), albeit in a different manner. Plants lacking DCP5 are more sensitive to ABA during germination, whereas lsm1a lsm1b and xrn4-5 mutants are affected at the early stages of vegetative growth. In addition, DCP5 and LSM1 regulate mRNA stability and act in translational repression of the main components of the early ABA signaling, PYR/PYL ABA receptors and SnRK2s protein kinases. mRNA decapping DCP and LSM1-7 complexes also appear to modulate ABA-dependent expression of stress related transcription factors from the AP2/ERF/DREB family that in turn affect the level of genes regulated by the PYL/PYR/RCAR-PP2C-SnRK2 pathway. These observations suggest that ABA signaling through PYL/PYR/RCAR receptors and SnRK2s kinases is regulated directly and indirectly by the cytoplasmic mRNA decay pathway.
Wawer I, Golisz A, Sulkowska A, Kawa D, Kulik A, Kufel J (2018) mRNA Decapping and 5′-3′ Decay Contribute to the Regulation of ABA Signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 9, 312